How to Build an AI Agent and Overcoming Common Workflow Challenges
- Alexia Palau

- Nov 18, 2025
- 7 min read
Sending personalized emails at scale can be a game changer for marketers, business owners, and job seekers. Automating this process with AI Agents saves time and improves outreach effectiveness.
Note that 90% of agent technology already existed 14+ years ago. I used to work for a Feed Management solutions company that supported some of the largest retailers in the UK with intelligent scraping, data structuring and data enrichment and improved the feeds that powered any Marketing channels that used them. An example would be Social Media carousels. Very little of AI agents is new in my opinion, but it is being democratized and provided by many today vs it being a more exclusive service offered by a few Tech companies back in the day (and part of GenAI as also new as well).
This post explains how to build two AI Automation Workflows using Make.com, Apify, Anymail Finder, Gemini, Gmail, and Google Sheets. It also shares practical solutions to common challenges encountered along the way.
Creating an AI Agent to Email Local Restaurants
The first AI Agent targets restaurants in your area to promote your services. This workflow combines data scraping, email discovery, AI-powered content generation, and Gmail integration.

Step 1: Collect Restaurant Data with Apify
Apify is a powerful web scraping tool that extracts structured data from websites. Use it to gather restaurant names, locations, and contact details from local directories or review sites. This data forms the foundation of your outreach list.
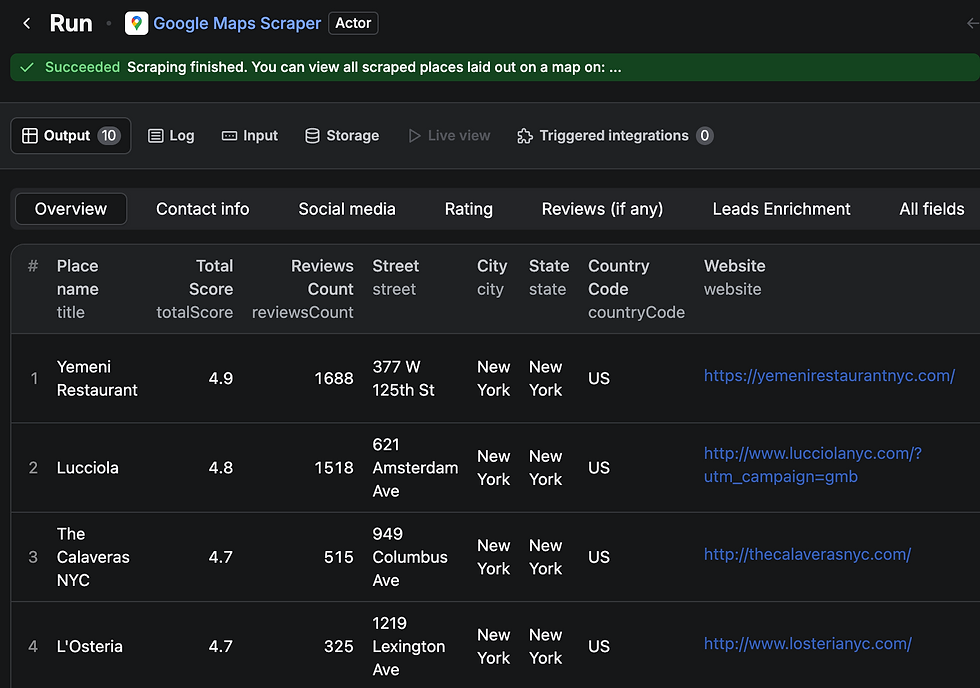
Add the Apify app in your Make.com workflow and add the API Key and Dataset ID. You will need to add API Keys across the workflow. Think of it as a path with doors. Every milestone will need a key that you will find inside of each app you want to connect.

Make sure you restrict the Apify data pull (I restricted to 10) and the Make.com data pull (to 8).



Step 2: Find Emails Using Anymail Finder
Once you have restaurant names and domains, Anymail Finder helps locate valid email addresses. It verifies emails to reduce bounce rates, ensuring your messages reach the right inboxes.
You will need to sign up, provide your details and start the 7 day free trial that you can use for a test or continue it if you'd like to use it after that amount of time. Connect the API.

Add the app to your Make.com workflow.

And create a filter to only pass on the results in the feed that contain websites, so Anymail Finder can look up email addresses tied to those domains.

Step 3: Generate Personalized Email Templates with Gemini
Connect to your Gemini app with the API Key. This is Google’s GenAI language model that can help you create customized email drafts that can include restaurant attributes like name and location. This is completely optional, you can have a template input or you can give it full freedom in the prompt to generate its own message, for example providing guidance around most common open rates to ensure that the message is engaging.


Make sure that the output is in plain text as otherwise you risk formatting inconsistencies when it is sent to you Gmail drafts folder. You add this to your prompt.

Map the attributes above (for example {location}) to the field names in the Apify feed. You are basically telling Gemini that when it finds in the prompt "{location}" it needs to find "Location" on the columns of the Apify feed pull.

And provide a "personality" to your GPT. Here you can include as much guidance as you want or your typical GPT guideline for tone of voice, etc.

You will need to add another filter from Anymail Finder to Google Gemini to ensure that when Gemini drafts the messages, it ties it back to an email address in order to create and place in your Drafts folder on Gmail.

You have to make sure the GPT model you are using is in line with the Service Tier you have. If you have the free version you will only be able to use certain models vs other Tiers. If you don't select the right one, it will block you from querying it or pulling the results you need from the Apify feed. This is how the error looks like in a different agent I built and it will also provide the link to the Tiers for you to be able to check what is the model aligned with your Tier:

Once you select the correct model for the Tier you have, it will pull the results you need. This choice prevents errors and unlocks all requested operations.



Step 4: Save Drafts in Gmail
Link your Gmail account to Make.com and send the AI-generated emails to your Drafts folder. This step allows you to review and tweak messages before sending, maintaining a personal touch.
No need for further filtering as the first two filters should be enough to get a clean set of emails in your Gmail. Connect the API Key, choose the folder it will send the messages to, map any attributes to the feed and it's all set.

Step 5: Run and Review
Run the workflow once to process all five restaurant contacts. Have a delinking approach because if you run the workflow across all apps you may run out of credits or as you may surpass the limit, trigger payment. When you delink each app (aside from putting results restrictions and filters) and make sure all work correctly in stages, this will help you to not waste credits.


Once tested, you can link the apps again and run the full workflow.
Check your Gmail Drafts folder to confirm the emails are ready to review and send.

Once you exit the Make.com scenario, don’t forget to save your workflow changes in to avoid losing progress.

Building an AI Agent to Email Your Contact List
The second AI Agent focuses on your existing contacts stored in Google Sheets. This approach is ideal for newsletters, updates, or personalized offers.
Step 1: Prepare Your Contact List in Google Sheets
Organize your contacts with columns for name, email, and any other relevant details. Clean data ensures smooth processing and this is very important in order for the agent to be able to pull the information you want easily. You can create milestones where the agent does the cleaning itself with filters but this can be inaccurate sometimes or cause errors and you might be better off correcting on Sheets.

Connect the Google Sheets app to the workflow, the API Key and select the location you want the agent to pull the data from.


Filter for the feed results that have emails and create the message template (if you want to use one) with Gemini.
Step 2: Use Gemini to Create Email Content
Same as the first Agent above (Restaurants). Make sure you are using the right Gemini model for the Service Tier you have. This keeps your messages relevant and engaging. Test the workflow by delinking it to ensure you don't surpass your credit limit or trigger payment.
Step 3: Connect Gmail to Save Drafts
Send the generated emails to Gmail Drafts for review. This step helps maintain control over your communication and prevents accidental mass sends.
Step 4: Execute and Verify
Run the connected workflow and verify that all drafts appear correctly in Gmail. Adjust templates if needed, then send emails manually. You can completely automate this to send on its own and dive into autonomous agentic workflows but proceed with caution.
Overcoming Common Workflow Challenges
Building AI Automation Workflows is rewarding but can present obstacles. Here are some issues and fixes encountered during setup:
Gemini Model Selection
The most frequent blocker was the Gemini model choice. Using a model outside your Google Workspace tier causes errors. Switching to Gemini 2.5 Flash, compatible with Tier 1, resolved this. Always check the Gemini API rate limits to match your subscription.
Attribute Mapping in Email Templates
Ensure that variables like Name and Location are correctly inserted in the email template. Incorrect mapping leads to generic or broken messages. Preview templates in Make.com before linking Gmail.
Saving Workflow Changes
A simple but costly mistake is forgetting to save changes in Make.com. Always save after edits to avoid losing hours of work.
Testing with Small Batches
Start with a small number of contacts (e.g., five) to test the workflow. This approach helps identify issues early without overwhelming your email system.
Tips for Effective AI Workflows
Keep templates clear and concise to improve response rates.
Regularly update your contact lists to maintain accuracy.
Monitor Gmail Drafts to catch errors before sending.
Document your workflow steps for easier troubleshooting and future improvements.
Final Thoughts on AI Agents for Email Outreach
These examples are a starting point, they are very basic and can be significantly upgraded for further autonomy and taking more interesting actions like:
Dynamic or intelligent scraping where you would scrape an e-commerce site for example for any new products being added and incorporated to Marketing channel feeds to enable them to be marketed as they are added to the website. This is how we did it 14+ years ago for large retailers with thousands of products and didn't know how to market new entries right away as the Marketing Team didn't have full visibility of new incorporated items and SKUs.
You can also incorporate payment actions with payment apps available on Make.com for example Stripe. And build a workflow that scrapes a website and buys a specific product at the lowest price.
And much more! I have just chosen to have a significant level of control over what I have built.
Building AI Agents is more daunting than difficult. You only need to get over the first step, build one, and you will see that the technology is not that new, it's a lot easier to figure out and it can help you understand how more advanced automation works. You can find a full walk through here.




Comments